SsangYong Rexton. Service manual - part 431
SSANGYONG Y200
1F2-44 M161 ENGINE CONTROLS
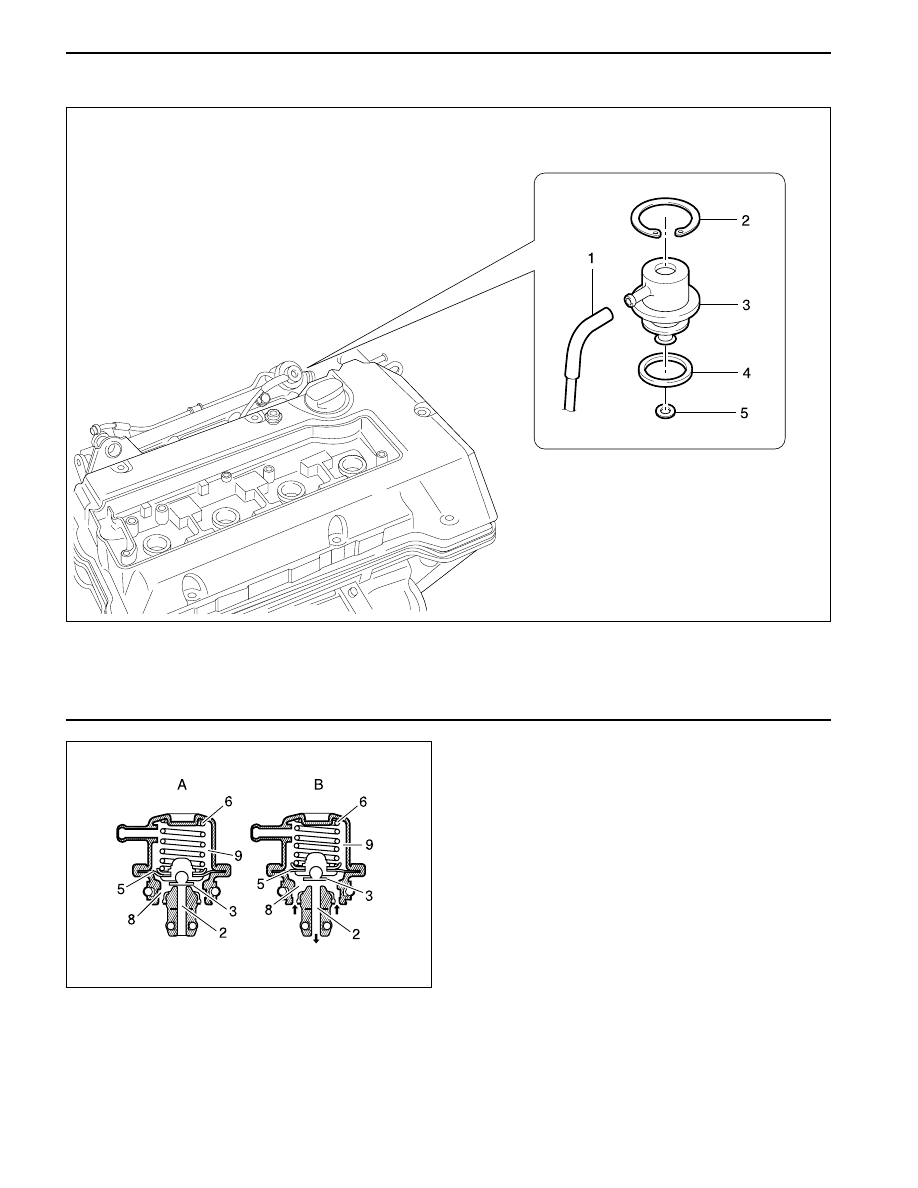
FUEL PRESSURE REGULATOR
YAA1F0F0
Function of the Fuel Pressure Regulator
The fuel pressure regulator maintains the fuel pressure
in the fuel line with the pressure of 3.2 bars to 3.8 bars
according to the intake manifold pressure. This
operating pressure cannot be changed, and the fuel
injection volume will be only determined by the injection
time. Over supplied fuel returns to the fuel tank through
the return line.
<Operating at full load>
There is no negative pressure applied to the spring
chamber (9) during the full load, and it is separated
from the fuel chamber (8) by the diaphragm (5).
When the fuel pressure goes up, the diaphragm forces
the compression spring (6) in the direction of
compression. At this moment, the valve (3) sticks to
the diaphragm by the fuel pressure, and the fuel return
line (2) opens. The fuel over supplied returns to the
fuel tank through the return line.
YAD1F360
2. Fuel return line
3. Valve
5. Diaphragm
6. Compression Spring
8. Fuel Chamber
9. Spring Chamber
1 Vacuum Hose
2 Circlip
3 Fuel Pressure Regulator
4 O-Ring
5 O-Ring
A. Valves Closed
B. Valves Opened