SsangYong Rexton. Service manual - part 54
DI04-29
CHANGED BY
EFFECTIVE DATE
AFFECTED VIN
EXHAUST SYSTEM
DI ENG SM - 2004.4
Y220_04026
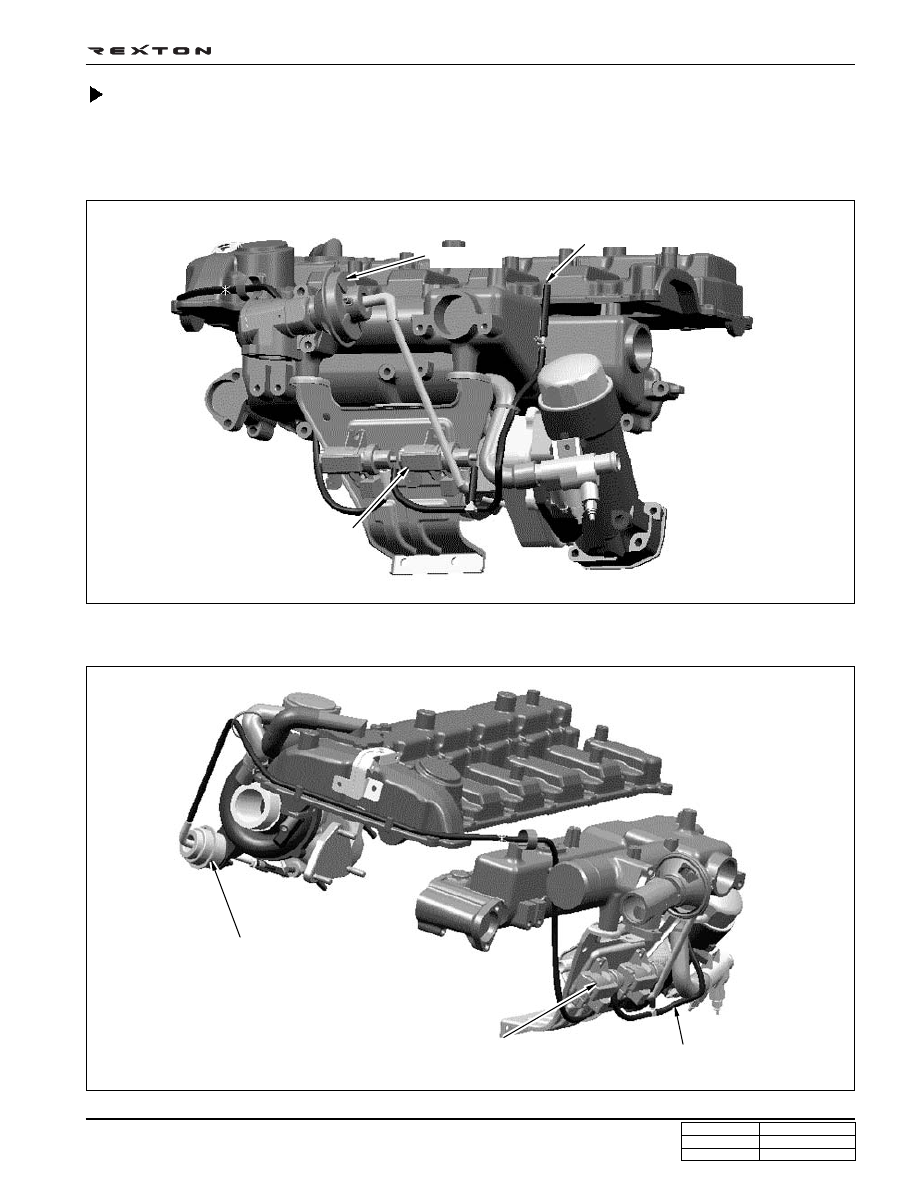
Vacuum Modulator and Vacuum Hose
Below figures illustrate vacuum hoses and related parts of EGR or turbo where wrong or poor connection of vacuum hose
would display condition of engine irregularity and defect diagnostic codes on the scan tool.
Related with EGR valve
Y220_04027
Related with turbo charger actuator
EGR valve
From vacuum pump
Vacuum modulator for
EGR valve control
Turbo charger pressure valve
Vacuum modulator for turbo
charger booster control
From vacuum pump