содержание .. 1 2 3 4 ..
Полупроводники. Каталог (2011 год) - часть 3
1/16
L6562
November 2005
1
Features
■
REALISED IN BCD TECHNOLOGY
■
TRANSITION-MODE CONTROL OF PFC PRE-
REGULATORS
■
PROPRIETARY MULTIPLIER DESIGN FOR
MINIMUM THD OF AC INPUT CURRENT
■
VERY PRECISE ADJUSTABLE OUTPUT
OVERVOLTAGE PROTECTION
■
ULTRA-LOW (
≤
70
µ
A) START-UP CURRENT
■
LOW (
≤
4 mA) QUIESCENT CURRENT
■
EXTENDED IC SUPPLY VOLTAGE RANGE
■
ON-CHIP FILTER ON CURRENT SENSE
■
DISABLE FUNCTION
■
1% (@ Tj = 25 °C) INTERNAL REFERENCE
VOLTAGE
■
-600/+800mA TOTEM POLE GATE DRIVER WITH
UVLO PULL-DOWN AND VOLTAGE CLAMP
■
DIP-8/SO-8 PACKAGES ECOPACK
®
1.1 APPLICATIONS
■
PFC PRE-REGULATORS FOR:
– IEC61000-3-2 COMPLIANT SMPS (TV,
DESKTOP PC, MONITOR) UP TO 300W
– HI-END AC-DC ADAPTER/CHARGER
– ENTRY LEVEL SERVER & WEB SERVER
2
Description
The L6562 is a current-mode PFC controller oper-
ating in Transition Mode (TM). Pin-to-pin compati-
ble with the predecessor L6561, it offers improved
performance.
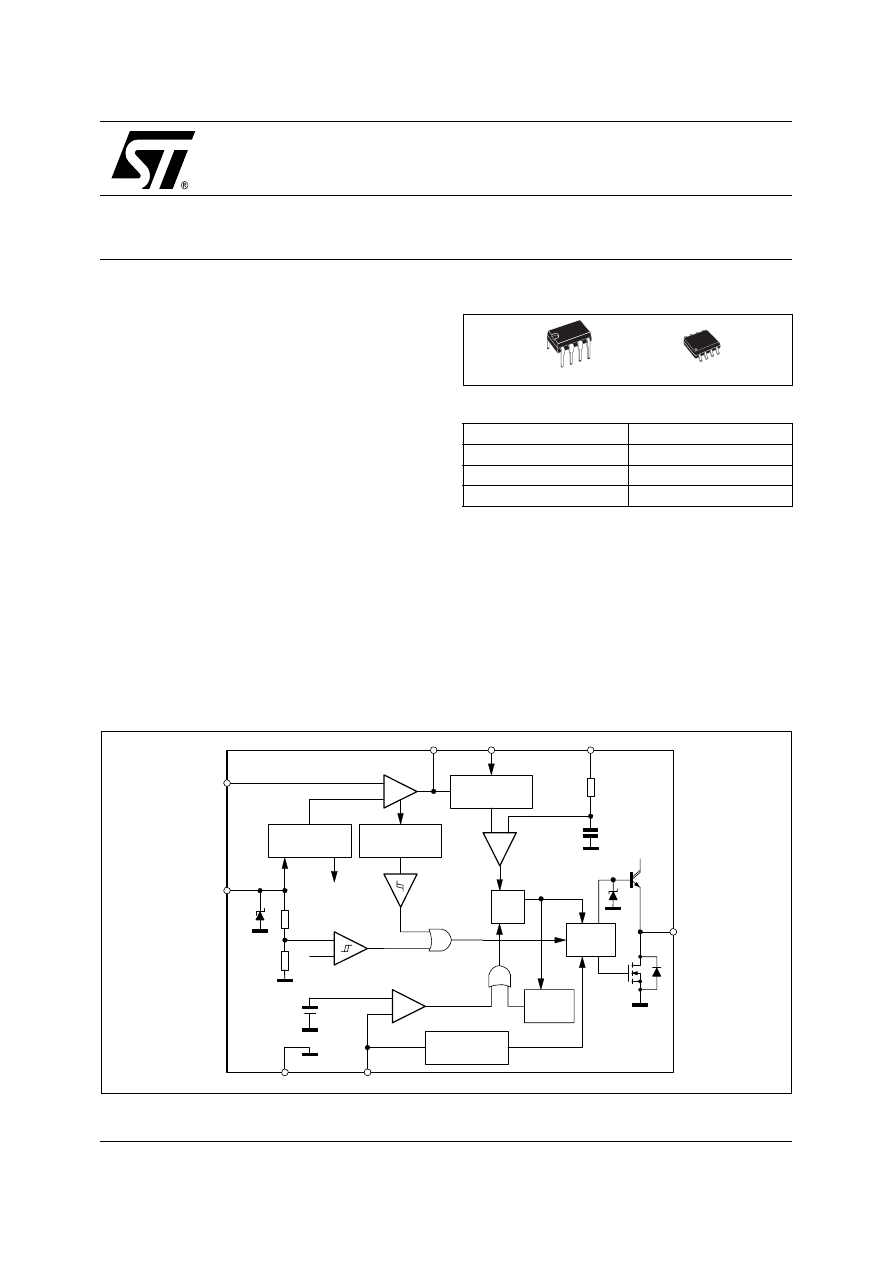
TRANSITION-MODE PFC CONTROLLER
Figure 2. Block Diagram
+
-
MULTIPLIER AND
THD OPTIMIZER
V
REF2
OVERVOLTAGE
DETECTION
VOLTAGE
REGULATOR
UVLO
INTERNAL
SUPPLY 7V
+
-
2.5V
R1
R2
R
S
Q
+
-
DRIVER
STARTER
+
-
ZERO CURRENT
DETECTOR
DISABLE
2.1 V
1.6 V
V
CC
8
1
2
3
4
ZCD
V
CC
INV
COMP
MULT
CS
GD
7
5
GND
6
25 V
40K
5pF
15 V
Starter
stop
Rev. 8
Figure 1. Packages
Table 1. Order Codes
Part Number
Package
L6562N
DIP-8
L6562D
SO-8
L6562DTR
Tape & Reel
DIP-8
SO-8