Ford Focus RS (2011 year). Manual - part 115
NOTE: A large quantity of water flows through the
water tank. If there are leaks in this area, it is
essential to ensure that the water drainage
mechanisms function correctly. Drainage openings
may not be blocked or stuck. Leaves and other dirt
must be removed before troubleshooting.
Corrective action
Before the actual repair, make sure that the water
drains are not blocked or stuck.
Remove the heater housing / ventilation and fit a
new Butyl sealing strip. Damaged sealing surfaces
must first be adjusted. A trapped carpet must be
removed.
Seal welds
PU sealing beads are applied to welded or riveted
connections Arrows to seal the interior of the
vehicle. Incorrectly applied or damaged seal welds
can allow moisture to penetrate into the interior of
the vehicle. It is also possible that sealing beads
whose shape and size appear to be intact actually
have poor adhesion.
Corrective action
Incomplete seal welds must be supplemented with
PU sealing compound. Damaged seal welds must
be removed and re-applied properly. Make sure
that any residual moisture is effectively removed
before a new seal is applied.
Attached parts
The add-on parts include:
• Exterior mirros, handles, controls.
• Mouldings, roof mouldings, lettering.
• Roof aerial, roof rack or connections for roof
rack systems.
• Bumper mountings.
• Injection nozzles, door contact switches, bump
stop rubber.
• Control unit seals.
• Tail lamps.
• All kind of screwed connections (pedal block,
door and tailgate hinges)
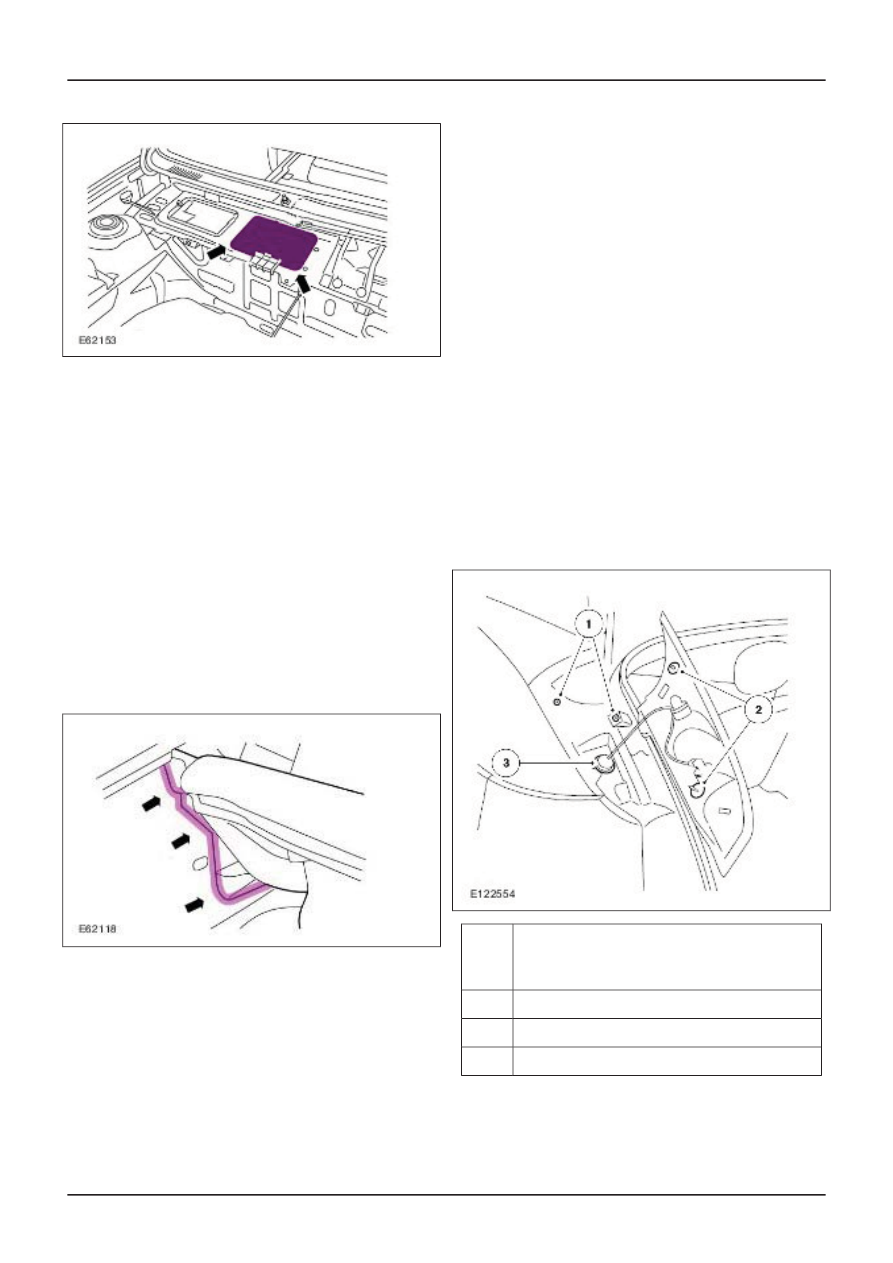
Example: Possible water entry points at the
rear lamp
Description
Des
cript
ion
Clips
1
Gaskets.
2
Rubber grommet
3
Add-on body parts must be fitted with seals,
grommets or sealing compound to prevent water
entry. However, even when a sealing system is
fitted, the screw thread may still cause leaks.
G468074en
501-25-
75
Body Repairs - General Information
501-25-
75
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION