Ford Focus RS (2011 year). Manual - part 116
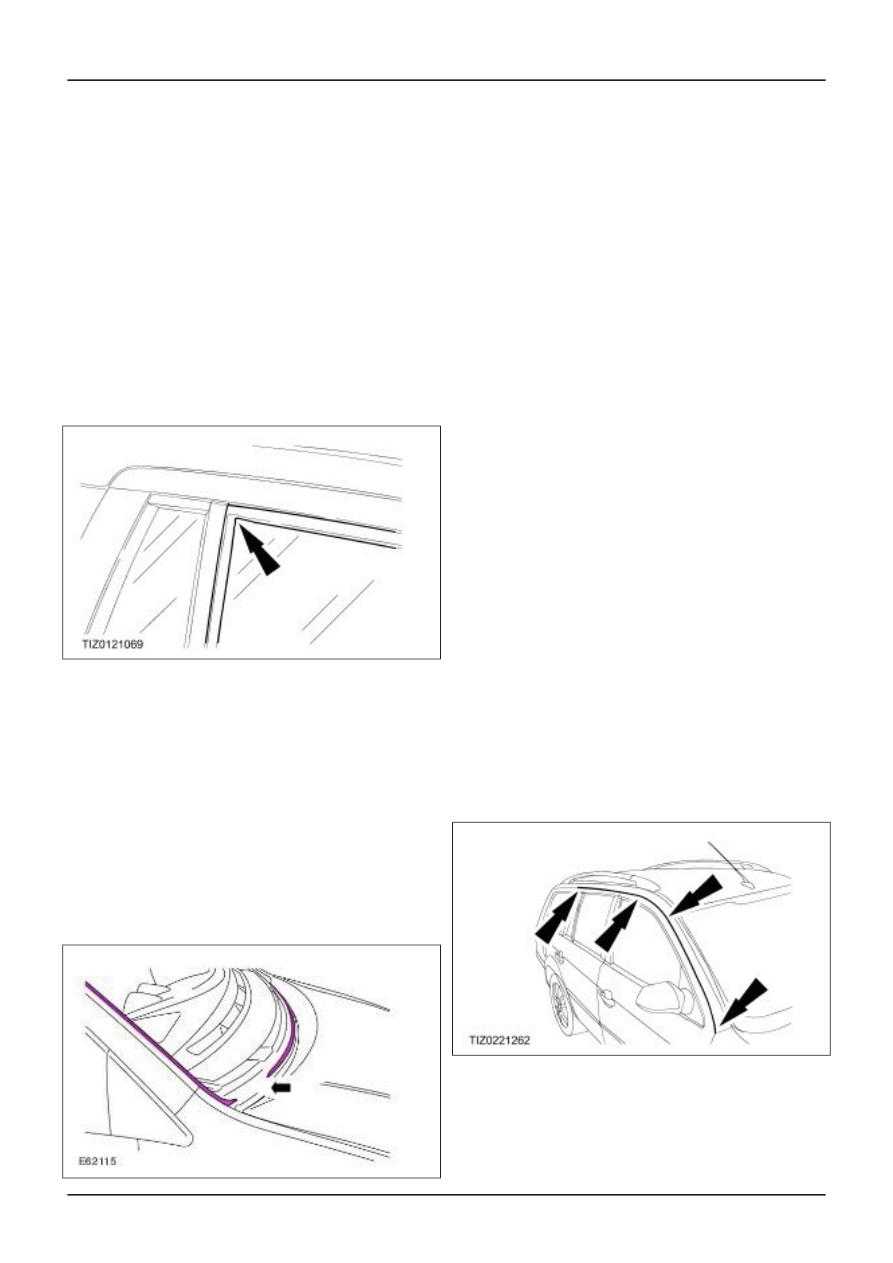
• Seals must be correctly installed. Special
attention must be paid at corners -arrow- that
the installation follows the contours.
• The seal must not show any kinks or folds or
any other damage.
• Seals must seal all around their circumference.
Gaps in seals result in openings which lead to
an increased incidence of noise. In this respect,
it is especially important to pay attention to the
seals in the area of the windows.
Remedial Action
Renew older seals which no longer have adequate
preload. Deformed or widened retaining flanges
must be reworked and provided with a new seal.
The corner areas -arrow- of a seal must be
properly seated. In some circumstances, a butyl
sealing strip must be affixed to support the sealing
at a corner.
Bonded joints
Glass is usually installed today using a bonded
joint. Gaps in the bonded joint can lead to noises
in the vehicle interior. If there are noises which are
believed to be associated with window glass, the
following points should be checked:
Gap in window bonding
• The window must be bonded without any gaps
-arrow-. Leaks can be found using the ultrasonic
tester or compressed air carefully blown from
inside onto the window glass bonding.
• The installed position of the window glass must
be correct. It must not have been bonded into
a position which is too low or offset to one side.
• The sealing or trim strips must fit tightly and the
glass must be mounted so that it is fully
enclosed. If a sealing or trim strip has not been
applied with enough pressure, high air speeds
can cause it to lift up. This can lead to wind
noises at higher speeds. Apply masking tape to
these areas for test purposes.
Corrective measures
Leaking areas of the window glass bonding
material can be sealed using PU sealing
compound. Pay special attention at the front
windshield, that any breaks in the bonding are not
too large. Otherwise the glass must be removed
and bonded in place again.
The installed location of a window glass cannot be
corrected. It must be removed and bonded into
place again.
Replace the trim strips or secure the lip seal using
PU adhesive.
Gaps, edges
Door gaps and edges are places where air
turbulence can form. This causes noises which can
be perceived as troublesome.
Gaps and edges - problem areas
Doors, hood and tailgate can cause wind noises
because of gaps -arrow- which are too large. If the
components are not installed flush to the bodywork
or the neighboring component, air break edges can
arise, which in turn can create a wind noise.
G468075en
501-25-
83
Body Repairs - General Information
501-25-
83
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION