SsangYong Rexton. Service manual - part 493
SSANGYONG Y200
4A-2 BRAKE SYSTEM
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
BRAKING SYSTEM TESTING
Brakes should be tested on a dry, clean, reasonably
smooth and level roadway. A true test of brake
performance cannot be made if the roadway is wet,
greasy or covered with loose dirt which can cause tires
not to grip the road unequally. Testing also will be
inaccurate on a crowned roadway because the wheels
tend to bounce.
Test the brakes at different vehicle speeds with both
light-and heavy-pedal pressure; however, avoid locking
the brakes and sliding the tires. Locked brakes and
sliding tires do not indicate brake efficiency since
heavily braked but turning wheels will stop the vehicle
in less distance than locked brakes. More tire-to-road
friction is present with a heavily braked, turning tire
than with a sliding tire.
There are three major external conditions that affect
brake performance:
•
Tires having unequal contact and grip of the road
will cause unequal braking. Tires must be equally
inflated and the tread pattern of the right and the
left tires must be approximately equal.
•
Unequal loading of the vehicle can affect the brake
performance since the most heavily loaded wheels
require more braking power and thus more braking
effort than the others.
•
Misalignment of the wheels, particularly conditions
of excessive camber and caster, will cause the
brakes to pull to one side.
HYDRAULIC BRAKE SYSTEM
BRAKE PEDAL
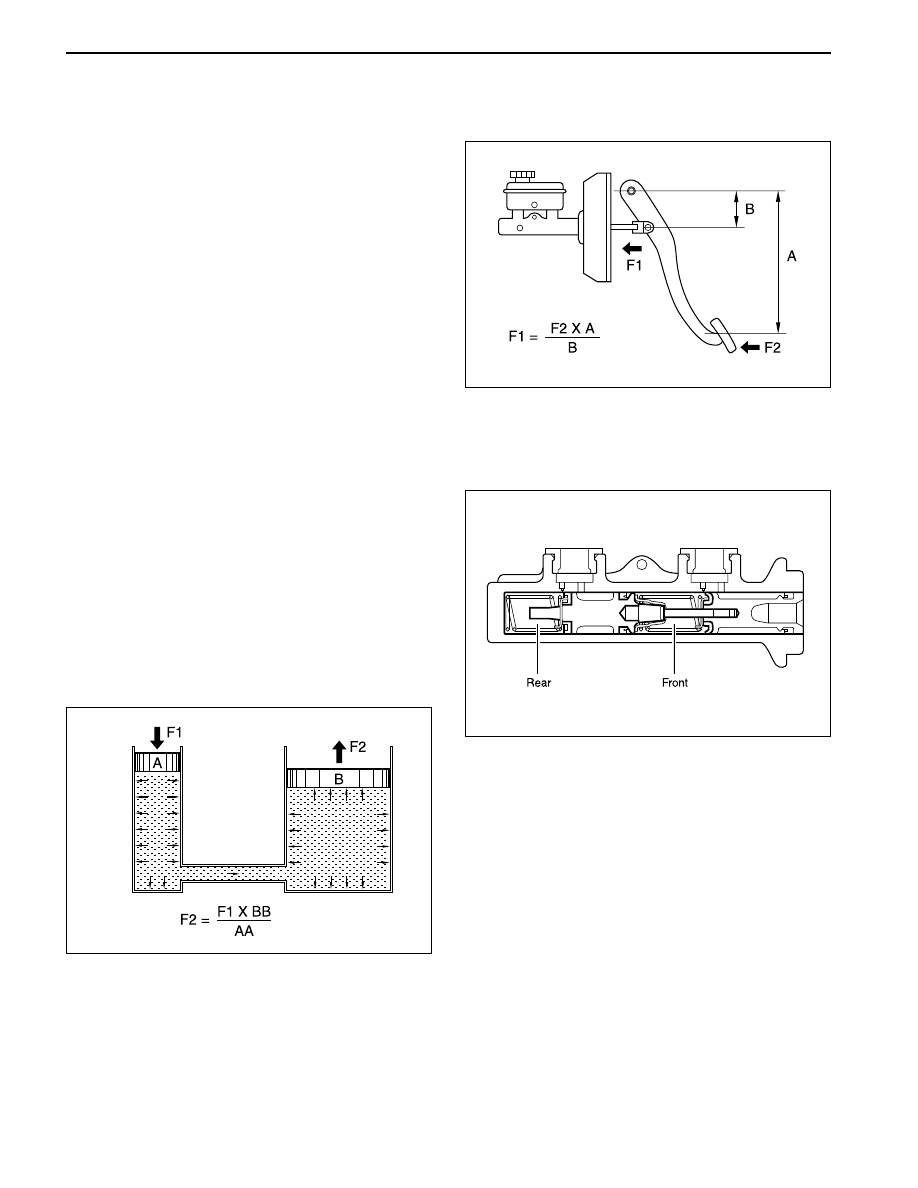
YAD4A010
This system uses the principle of the leverage and
PASCAL’s. When you pushes the brake pedal, the
pressure by adapting the pedal increases through the
power booster and delivers it into the master cylinder
to generate hydraulic pressure.
Hydraulic pressure generated by the master cylinder
delivers to the caliper through the brake pipe or hose.
This hydraulic pressure allows the caliper pad to push
the disc plate. Thus it generates the braking forces.
YAD4A020
Brake pedal uses the principle of the leverage and
increases the pressure into the master cylinder in order
to generate the braking forces.
MASTER CYLINDER
The master cylinder is designed for use in a diagonally
split system. One front and one diagonally opposite
rear brakes are served by the primary piston. The
opposite front and rear brakes are served by the
secondary piston.
The master cylinder incorporates the functions of the
standard dual master cylinder, plus a low fluid level
indicator and the proportioning valves in the non-
antilock braking system. The proportioning valves limit
the outlet pressures to the rear brakes after a
predetermined master cylinder pressure has been
reached. The brake master cylinder sensor is attached
under the body of the plastic brake master cylinder
reservoir.
YAD4A030