SsangYong Rexton. Service manual - part 447
SSANGYONG Y200
1F3-8 DIESEL ENGINE CONTROLS
YAD1FAG0
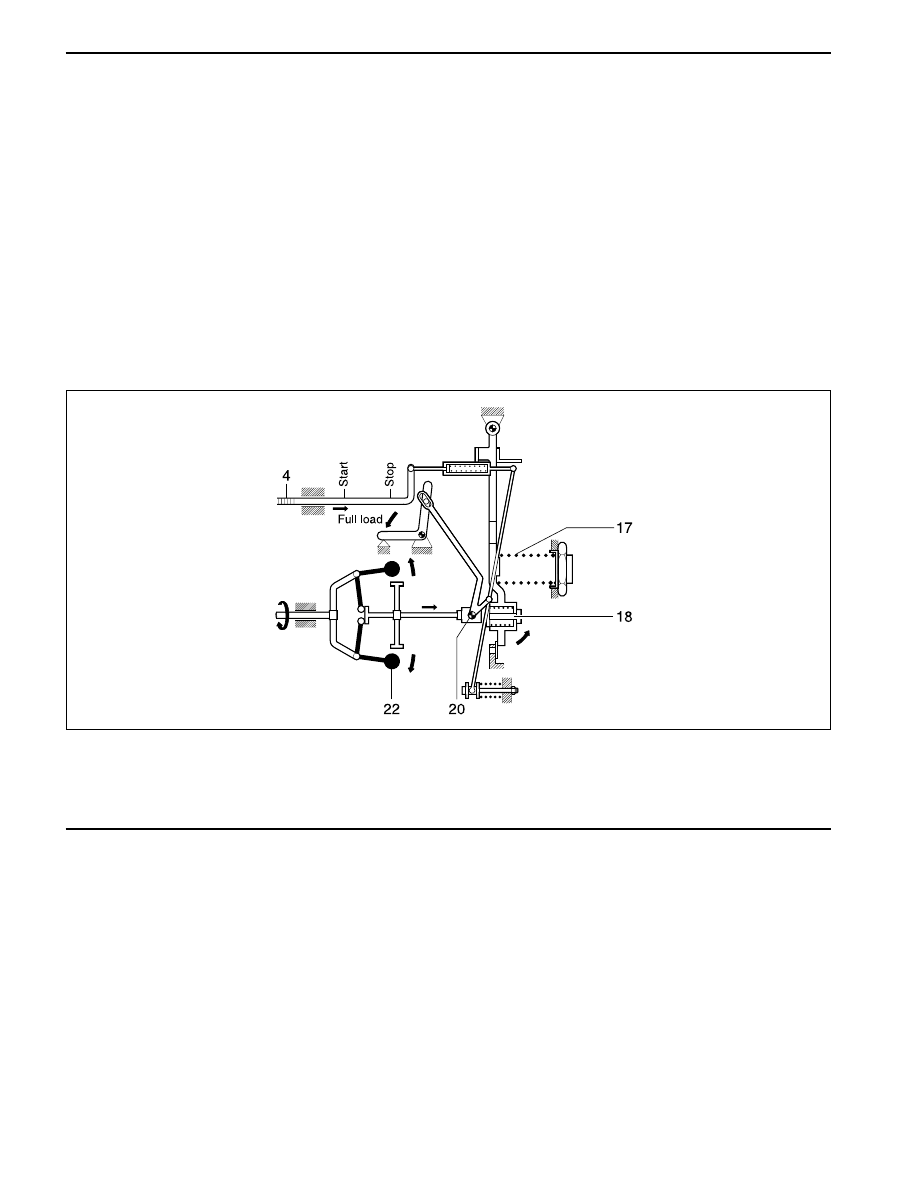
Torque control
If torque control is fitted, full-load delivery quantity is
reduced when a given speed n
1
is exceeded, because
centrifugal force acting on sliding sleeve (20) exceeds
the force of the torque-control spring fitted in spring
retainer (18). The torque-control spring yields to this
force. As a result, if speed increases further, control
rack (4) shifts by the torque-control travel distance.
Torque control ends at speed n
2
.
Instead of positive torque control, the RDF governor
can have negative torque control. Here the control-rack
setting is controlled by a spring combination.
High idle (maximum) speed
With the accelerator pedal pressed to the floor, the
full-load quantity is injected until the maximum full-
4 Control Rack
17 Governor Spring
18 Spring Retainer (Torque Control)
Full-load setting
(only the components concerned in the governing process are shown)
20 Governor Sliding Sleeve
22 Flyweight
load speed n
vo
is reached. If engine speed increases
beyond full-load speed, the force exerted by the
flyweights (22) suffices to overcome the force of
governor spring (17) and full-load-speed regulation
starts.
Engine speed increases slightly, and rack travel is
reduced due to the rack being moved towards stop
(shutoff) and the delivery quantity decreases.
Breakaway depends upon governor spring pretension.
The engine adjusts to high idle (maximum) speed n
10
when all load is removed.
When driving downhill with the accelerator released,
the vehicle drives the engine (overrun) and accelerates
it.
No fuel is injected during this operating mode (overrun
fuel shutoff).