Ford Focus RS (2011 year). Manual - part 106
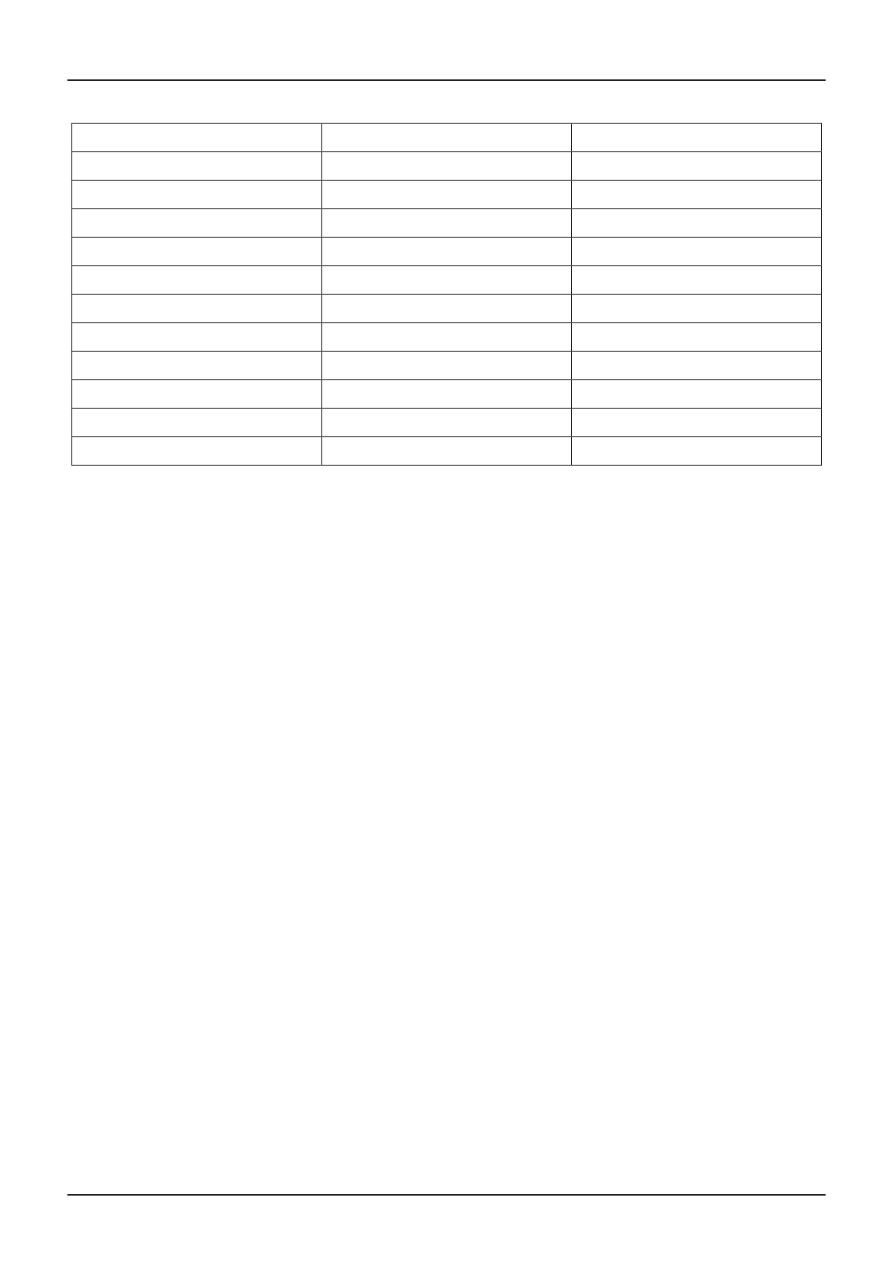
Specification
Finis Code
Description
-
5 030 492
Underbody protection
WSK-M7C89-A
1 219 834
Anti-corrosion wax
-
5 030 081
Cavity wax
S-M3G4620-A
1 128 983
Profiled butyl seal
-
1 205 996
Weld primer
WSK-M4G245-B
1 136 479
Clinched flange protection
WSS-M4G364-A
1 205 817
Seam sealing compound
-
1 143 255
Body sealing compound
-
1 203 241
Metal adhesive kit
WSK-M4G329-A
1 613 838
Windshield sealant
-
1 219 837
Adhesive spoiler set
G468061en
501-25-
3
Body Repairs - General Information
501-25-
3
SPECIFICATIONS