SsangYong Rexton. Service manual - part 541
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION 5A-35
SSANGYONG Y200
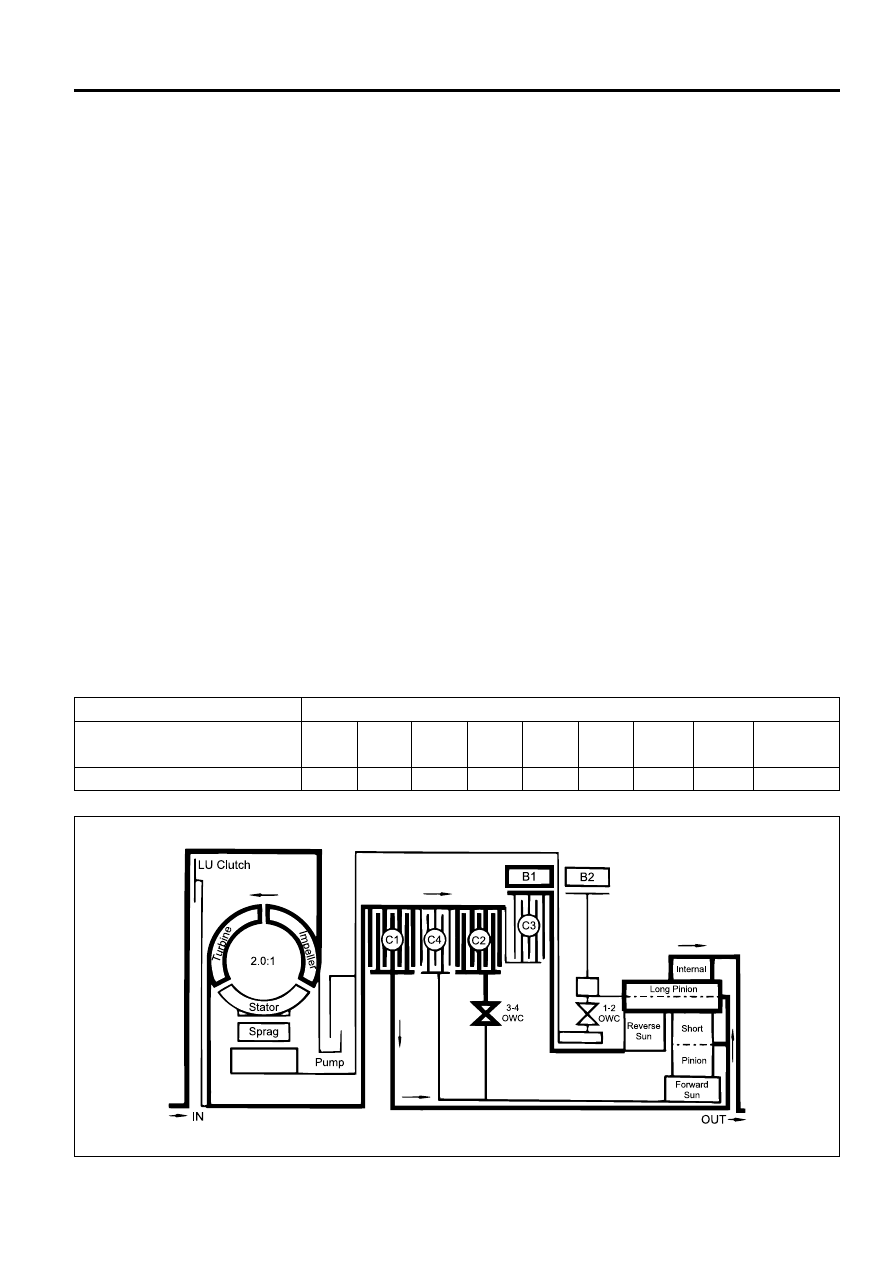
Power Flow - Drive 4 (Overdrive)
In Drive 4 (Overdrive), transmission drive is via the
input shaft to the forward clutch cylinder.
The elements of the transmission function as follows;
•
The C1 clutch is applied to drive the planet carrier
clockwise.
•
The B1 band is applied to hold the reverse sun gear
stationary.
•
As the planet carrier tuns, the long pinion walks
around the stationary reverse sun gear and rotates
around its axis driving the internal ring gear and
output shaft in a clockwise or forward direction at a
speed faster than the input shaft i.e. in overdrive
ratio.
•
The forward sun gear is also driven faster than the
input shaft and overruns the 3-4 OWC.
•
The C2 clutch is engaged to reduce the speed differ-
ential across the 3-4 OWC.
Control
To maintain this arrangement in the steady state sole-
noids and valves are activated as follows;
•
Solenoid S1 is switched ON. S2 is switched OFF.
•
With S1 switched ON, the 3-4 shift valve is held in
the fourth gear position by line 500 pressure on the
small end of the valve.
•
With S2 switched OFF, the 2-3 shift valve is held in
the fourth gear position by line 500 pressure on the
large end of the valve.
•
The 1-2 shift valve is held in the fourth gear position
by S2 oil pressure.
•
2nd oil (line pressure) from the 1-2 shift valve is di-
rected to the band apply feed regulator valve, and
to the 2-3 shift valve.
•
The band apply feed regulator valve supplies 2nd
oil (regulated to line pressure multiplied by the valve
ra-tio) to the Band Apply Feed (BAF) circuit.
•
Band apply feed oil is directed to;
- the outer apply area of the front servo
- the inner apply area of the front servo piston via
the 3-4 shift valve
- the 1-2 shift valve to provide an exhaust port
when the transmission is shifted to first gear
•
2nd oil at the 2-3 shift valve is directed to the 3rd
oil circuit.
•
3rd oil from the 2-3 shift valve is directed to the
clutch apply regulator valve, and to the 4-3
sequence valve.
•
The clutch apply regulator valve supplies oil (regu-
lated to line 500 pressure multiplied by the valve
ratio) to the Clutch Apply Feed (CAF) circuit.
•
The CAF oil is directed to;
- the C1 clutch
- the 4-3 sequence valve
•
Drive oil (line pressure) from the manual valve en-
gages the C2 clutch.
KAA5A460
Gear State
Drive 4 Overdrive
C1
X
C2
X
C3
-
C4
-
B1
X
B2
-
1-2
OWC
-
3-4
OWC
-
LU
CLUTCH
-
ELEMENTS ENGAGED