SsangYong Rexton. Service manual - part 511
ABS AND TCS 4E-3
SSANGYONG Y200
TRACTION CONTROL SYSTEM
(TCS) DESCRIPTION
General Information
The traction control system (TCS) is a traction system
by means of brake intervention only, available in a low
speed range (< 60 kph).
It works on µ-split roads with sidewise different friction
coefficients.
The spinning driven wheel is braked and the drive
torque can be transferred to the wheel on the high-µ
side. During TCS active, the TCS information lamp is
blinking.
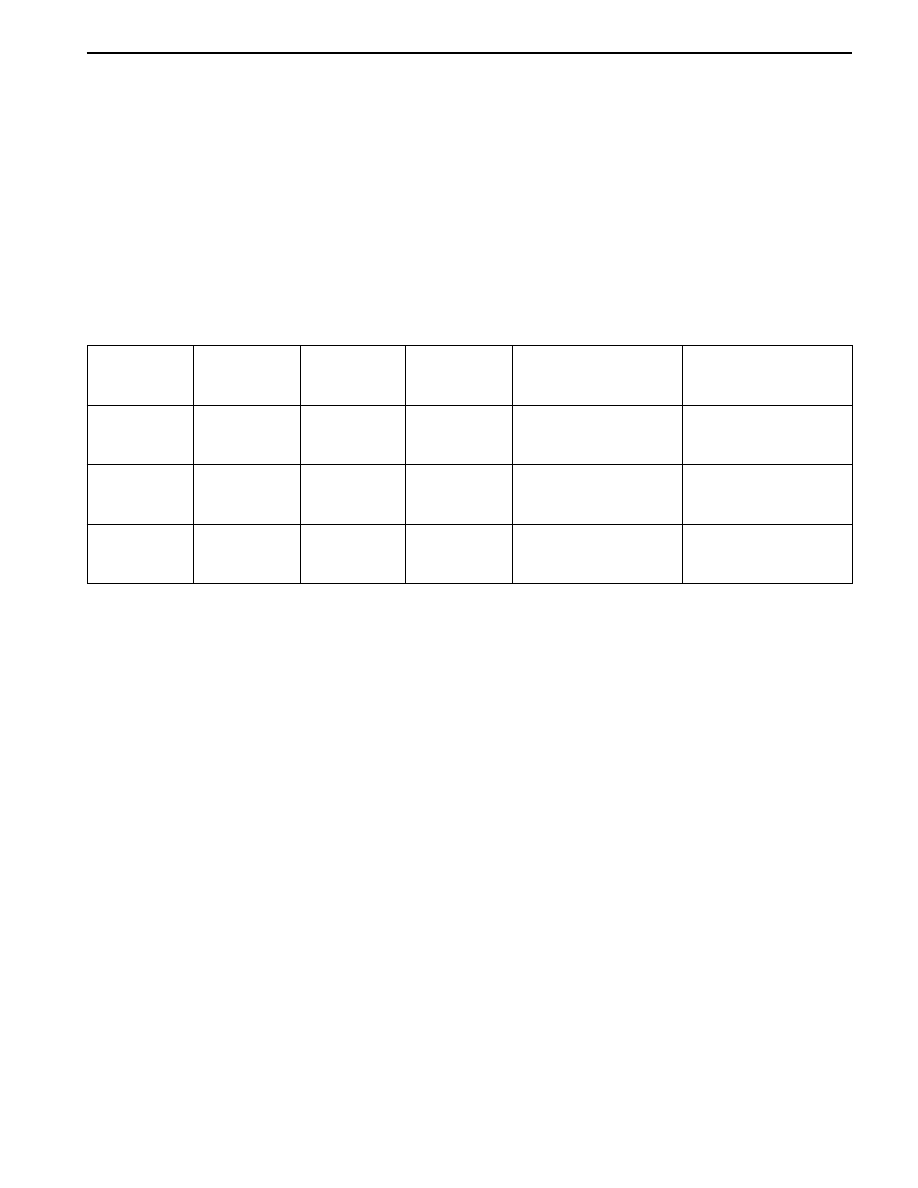
System Failure (EBD,
ABS or TCS are Not
Distinguished)
ABS Warning
Lamp
Ignition ON
ABS
Operation
TCS
Operation
TCS Passive Due to
Temperature Model
2 second on
for lamp
check
OFF
OFF
ON
OFF
TCS Info
Lamp
2 second on
for lamp
check
OFF
Blinking
(FLASHING)
OFF
ON
EBD Warning
Lamp
2 second on
for lamp
check
EBD
operation/OFF
OFF
ON
OFF
The temperature of the brakes is calculated by a
mathematical model and TCS is switched passive if
the calculated temperature is greater than a threshold
value (500 °C). TCS is permitted again, when the
calculated temperature is less than 350 °C.
Lamp Concepts
The system is equipped with an TCS information lamp,
which is blinking during TCS operation.
The activation of the EBD, TCS warning lamp and the
TCS info lamp is summarized in the following table: