Mazda B4000 Truck (2007 year). Manual - part 7
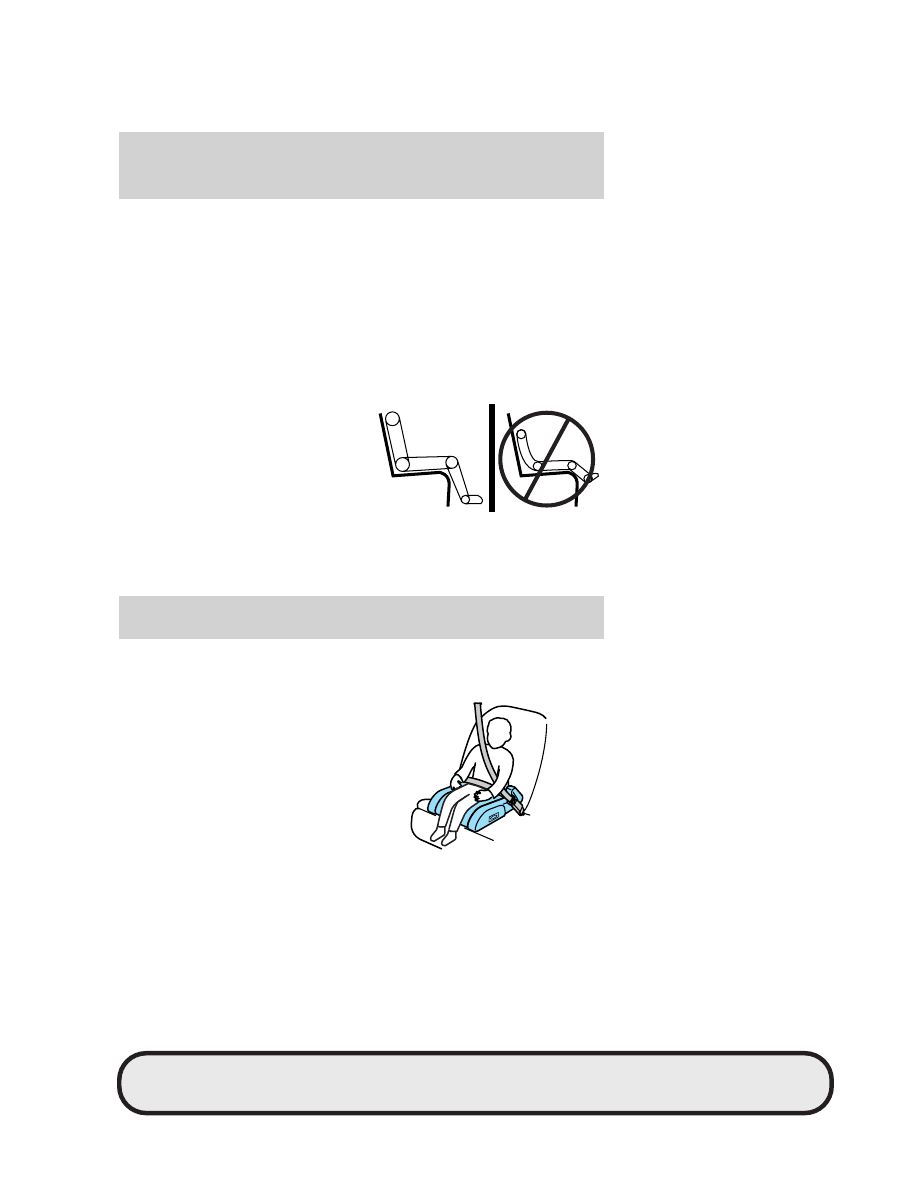
Booster seats position a child so that safety belts fit better. They lift the
child up so that the lap belt rests low across the hips and the knees
bend comfortably. Booster seats also make the shoulder belt fit better
and more comfortably for growing children.
When children should use booster seats
Children need to use booster seats from the time they outgrow the
toddler seat until they are big enough for the vehicle seat and
lap/shoulder belt to fit properly. Generally this is when they weigh about
80 lb. (about 8 to 12 years old).
Booster seats should be used until you can answer YES to ALL of these
questions:
• Can the child sit all the way back
against the vehicle seat back with
knees bent comfortably at the
edge of the seat without
slouching?
• Does the lap belt rest low across the hips?
• Is the shoulder belt centered on the shoulder and chest?
• Can the child stay seated like this for the whole trip?
WARNING: Booster seats must be installed only in seating
positions equipped with a combination lap/shoulder belt.
Types of booster seats
There are two types of belt-positioning booster seats:
• Those that are backless.
If your backless booster seat has a
removable shield, remove the
shield and use the lap/shoulder
belt. If a seating position has a
low seat back and no head
restraint, a backless booster seat
may place your child’s head (top
of ear level) above the top of the
seat. In this case, use a
high-backed booster seat.
art=cgrss526_b
art=mbsss109_a
REVIEW COPY ——
2007 B-Series (mbs), Owners Guide (post-2002-fmt) (own2002), Market: USA (fus)
PAGE: 101 OP: root EDIT SESSION: 1 DATE: AUG 3 2006 at 11:45 JOB: @ibm2/ford_pdm/CLS_ford/GRP_own2002/JOB_mbs/DIV_og
Seating and Safety Restraints
101