Buick Lucerne (2009 year). Instruction - part 21
To adjust the vertical aim:
1. Open the hood. See Hood Release on page 5-13
for more information.
2. Locate the aim dot on the lens of the low-beam
headlamp.
3. Record the distance from the ground to the aim dot
on the low-beam headlamp.
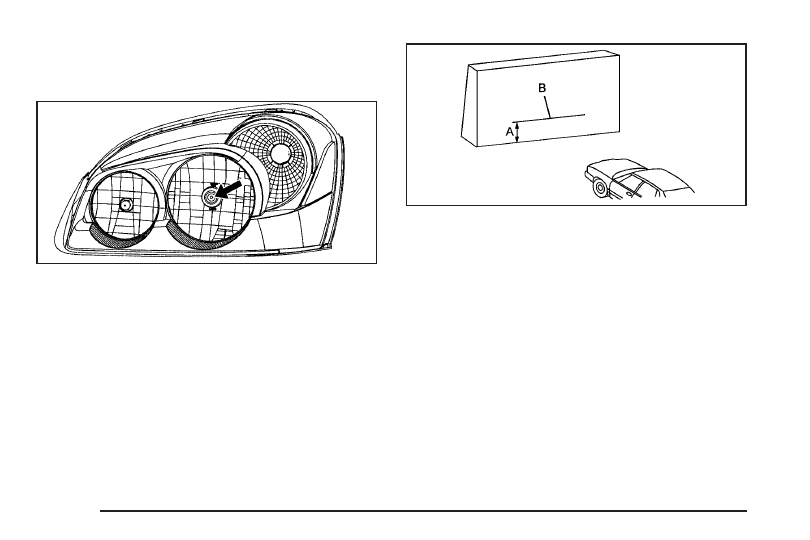
4. At a wall, measure from the ground upward (A) to
the recorded distance from Step 3 and mark it.
5. Draw or tape a horizontal line (B) on the wall the
width of the vehicle at the height of the mark in
Step 4.
Notice: Do not cover a headlamp to improve beam
cut-off when aiming. Covering a headlamp may
cause excessive heat build-up which may cause
damage to the headlamp.
6. Turn on the low-beam headlamps and place a
piece of cardboard or equivalent in front of the
headlamp not being adjusted. Do not place directly
on the headlamp. This allows only the beam of
light from the headlamp being adjusted to be seen
on the flat surface.
5-52