SsangYong Stavic / SsangYong Rodius (2005 year). Service manual - part 415
ABS/ESP SYSTEM
STAVIC - 2004.09
43
4K
CHANGED BY
EFFECTIVE DATE
AFFECTED VIN
Working voltage
Max. output current
Detected max. angular velocity
Working temperature
Supplying voltage
When short
When short to sensor
Output voltage (HI)
Output voltage (LO)
9 ~ 16 V
10 mA
1500°/S
-30 ~ 75°C
9 ~ 16 V(battery voltage)
0V
Power voltage - 0.7 V
Approx. 3.50 V (3.0 ~ 4.1 V)
Approx. 1.50 V (1.3 ~ 2.0 V)
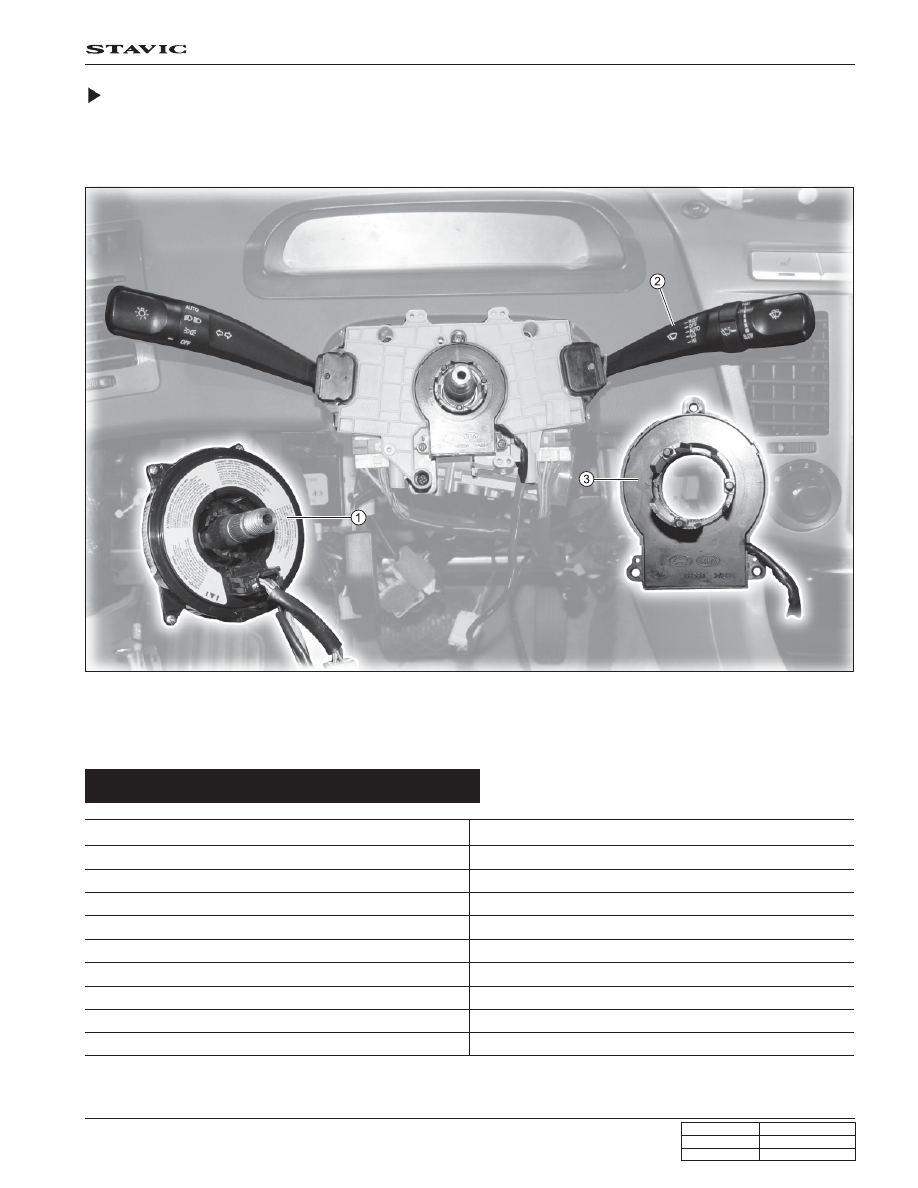
SWAS : Steering Wheel Angle Sensor
The steering wheel angle sensor is located between clock spring and multifunction switch. This sensor is used for
recognition of driver’s intends. If the sensor is replaced with new one, it can detect the neutral position after the vehicle
is moving over 20 km/h for more than 5 seconds.
1. Clock spring
2. Multi-function switch
3. SWAS (Steering Wheel Angle Sensor)
Specifications
Descriptions
Specifications