Snowmobile Polaris Two Stroke (2007 year). Instruction - part 13
2.9
GENERAL
2
Measurement Conversion Chart
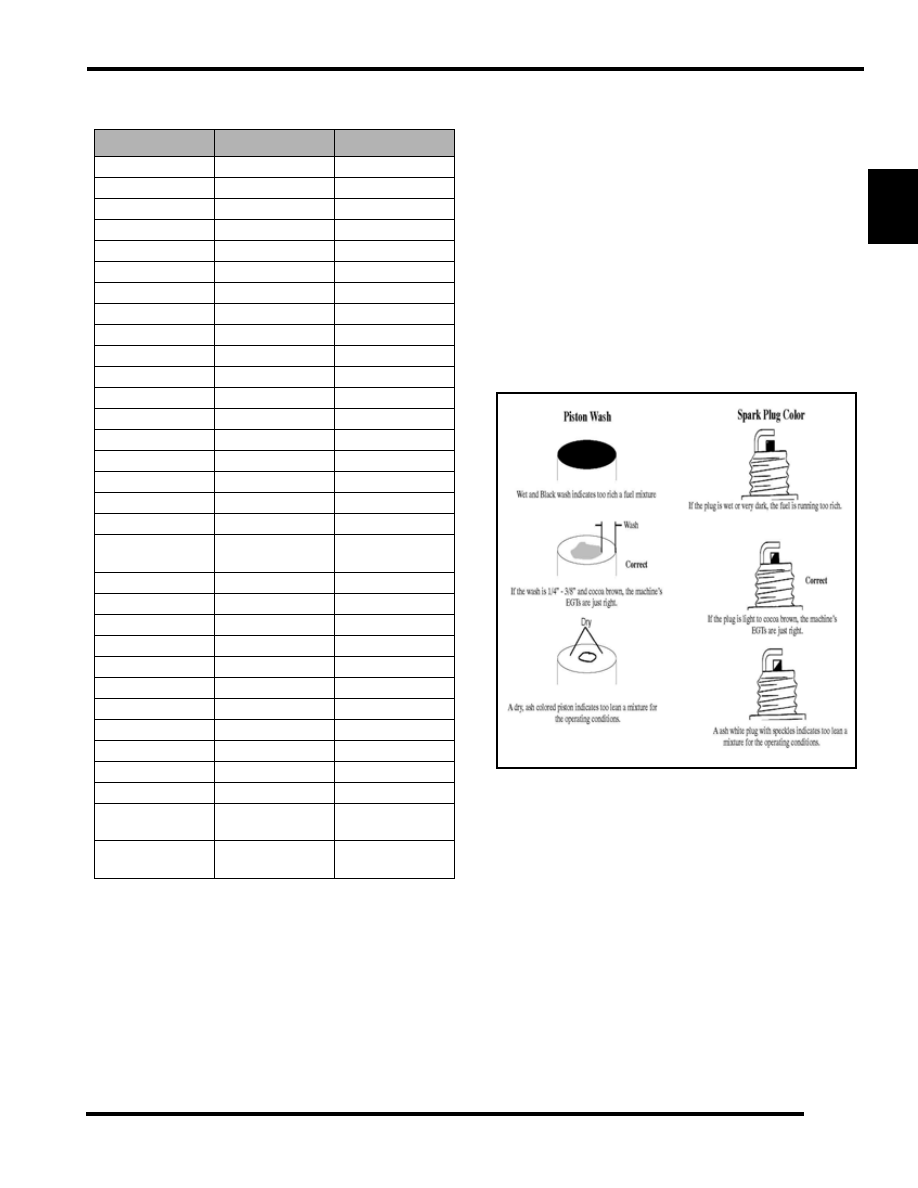
Piston Wash / Spark Plug Reading
Changing temperature, barometer, altitude, and fuel supply are
just a few of the factors that can affect the day to day
performance of your engine. That is why using Exhaust Gas
Temperatures (EGT) are important for maintaining optimum
performance. There are two methods for helping you determine
what the EGTs are for your machine. Piston wash and the
coloring of your spark plug.The piston wash is by far the most
valuable tool in concluding EGTs, with the spark plug color
running a distant second. Use the illustrations below to help you
establish the EGTs for your machine.
Once the proper jetting is established, you can reference the
EGT gauge for your baseline numbers. Then, if there is a rise or
fall of 25 degrees, you must jet accordingly to return your EGTs
to the baseline numbers.
U
NIT
OF
M
EASURE
M
ULTIPLIED
BY
C
ONVERTS
TO
ft-lb
x 12
= in-lb
in-lb
x.0833
= ft-lb
ft-lb
x 1.356
= N-m
in-lb
x.0115
= kg-m
N-m
x.7376
= ft-lb
kg-m
x 7.233
= ft-lb
kg-m
x 86.796
= in-lb
kg-m
x 10
= N-m
in
x 25.4
= mm
mm
x.03937
= in
in
x 2.54
= cm
mile
x 1.6
= km
km
x.6214
= mile
Ounces (oz)
x 28.35
= grams (g)
grams (g)
x.035
= Ounces (oz)
cc’s
x.03381
= Fluid Ounces (oz)
lbs
x.454
= kg
kg
x 2.2046
= lbs
Cubic Inches
x 16.387
= Cubic
Centermeters
Cubic Centimeters
x.061
= Cubic Inches
Imperial pints
x.568
= liters (l)
liters (l)
x 1.76
= Imperial pints
Imperial quarts
x 1.137
= liters (l)
liters (l)
x.88
= Imperial quarts
Imperial quarts
x 1.201
= US quarts
US quarts
x.833
= Imperial quarts
US quarts
x.946
= liters
liters
x 1.057
= US quarts
US gallon
x 3.785
= liter
liter
x.264
= US gallon
Pounds force per
square inch (psi)
x 6.895
= Kilo pascals (kPa)
Kilo pascals (kPa)
x.145
= Pounds force per
square inch (psi)